In this post I will be showing you a stepwise procedure to make
the DataGridView height automatic i.e. increase with the number of rows added.
Context:
a)Given
that multiple of rows are required in DataGridView but you are unknown about
how many rows are required.
b)You want your DataGridView
height increased automatically when new row(s) are/is added.
Context example: You are to provide user to names of his friends in his classroom with their
some detail like age, sex, etc. and etc. Now, the problem is you don’t know how
many friends he has in his classroom; maybe 10 or 20 or 30 or 31. Let’s
suppose, you want to use DataGridView to show all data the user has entered. There
is no problem when you add the data in DataGridView by adding rows in it, but
the problem arises when your DataGridView height is not sufficient to show all
rows in it; you will see vertical scrollbar in the side of DataGridView
afterward. You want to show all rows (whatever the number of rows datagridview
has) without scrollbar (i.e. see all rows without scrolling down like a table).
Here, you can use my concept.
When DataGridView height is not automated:
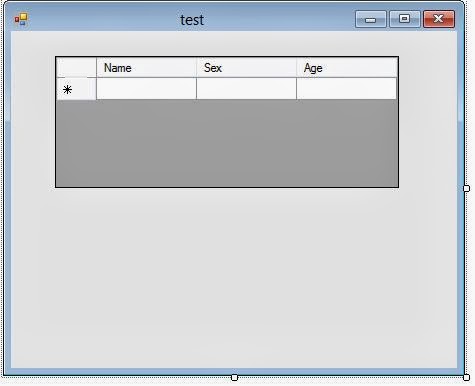 |
| Fig 1: Form Design View |
Now I am adding 10 sample data programmatically (from
coding) and running the program.
 |
Fig 2: Form running view where you can clearly see the scrollbars in side of the DataGridView
|
 |
| Fig 3: Form running view. You can see that when DataGridView size is more than the extra space below the table is shown. Note: Size is changed manually in design view |
 |
| Fig 4: Form running view after the height is made automatic. |
Context solution: Increase
DataGridView height automatically when new rows are added.
Here goes the solution for this problem:
11)Create a DataGridView and add columns.
22)Create a new Sub (copy paste below)
Private Sub
DataGridView1_RowsAdded(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As
System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewRowsAddedEventArgs) Handles
DataGridView1.RowsAdded
End Sub
# This Sub handles the event when
rows are added in DataGridView1
#Note: You can create this Sub by double
clicking the DataGridView and going to coding section of Form and clicking the
combo shown below and selecting ‘RowsAdded’. Be careful don’t click anywhere
else after double clicking the DataGridView (or jus remain in the sub where
double click takes you and then click combo)
 |
| Fig 5: Combo location in code view to add the Sub |
33)Now, add code below in Sub created in step 2
DataGridView1.Height
= DataGridView1.Height + DataGridView1.Rows(DataGridView1.Rows.Count -
1).Height
# It
changes the DataGridView height by adding the height of row added.
#Note:
this is not sufficient to make dataGridView look like in fig 4.
44)Now, add the below code in form
load Sub; just below the declaration of Sub:
DataGridView1.Height
= DataGridView1.ColumnHeadersHeight + 24
#like below:
Private Sub
test_Load(ByVal sender As
System.Object, ByVal
e As System.EventArgs)
Handles MyBase.Load
DataGridView1.Height =
DataGridView1.ColumnHeadersHeight + 24
End Sub
#24 is added because
there will be an extra row to add data in the DataGridView (see row with header
*) which size is 22px and 2px extra is for the margin of the DataGridView. If ‘add
data’ is not enabled in dataGridView than use 2. Check yourself by changing the
value.
 |
Fig 6: when new data is being added in DataGridView from Fig 4.
#Note: 10 data are added programmatically.
|





